The new solutions from Toshiba target high-power and industrial motor applications.
Toshiba recently introduced a slew of new motor-control facing solutions, including new Arm Cortex-M4-based microcontrollers and a 50-V brushed DC motor driver IC. Together, these devices may provide engineers with tools to simplify system design and improve efficiency and precision for high-power motor applications.

Toshiba is adding new devices to two groups in its MCU TXZ family.
Additions to Two Motor Control MCU Families
Toshiba has expanded its lineup of Arm Cortex-M4-based microcontrollers for motor control applications with the new M470 and M4K group devices .
The one new addition to the M470 family is the TMPM471F10FG (datasheet linked), which operates at up to 160 MHz and integrates a high-performance floating-point unit (FPU) and a memory protection unit (MPU). The model supports up to two motor control functions, facilitated by Toshiba’s Advanced Programmable Motor Driver (A-PMD).
The M470 device further improves on previous models by incorporating 1 MB of Flash memory, which effectively doubles the storage capacity while maintaining a program/erase cycle endurance of up to 100,000 times. Other noteworthy features include 64-KB RAM, multiple serial communication interfaces, and two 32-bit advanced encoder input circuits.
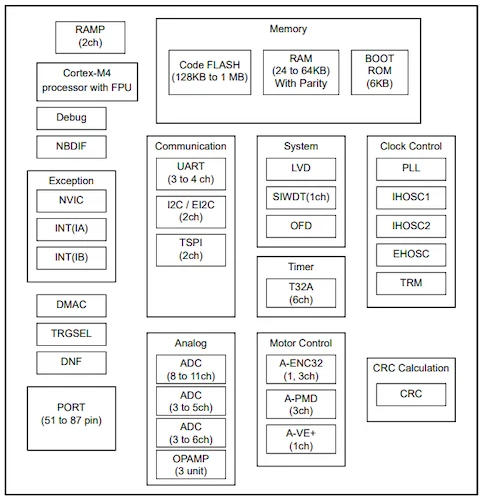
TMPM4K group block diagram.
The six new M4K microcontrollers, on the other hand, are designed for both main system control and motor control. Operating at a maximum clock frequency of 120 MHz, these microcontrollers also share the MPU and FPU features of the M470 family but instead, come equipped with 128 KB to 256 KB of Flash memory and up to 18 KB of RAM. The M4K solutions are distinct from the M470 solutions because they include an operational amplifier and a dedicated I2C interface and come in package sizes, including LQFP64, LQFP48, and LQFP44.
Both groups share other features, such as 32-bit timer event counters, two 12-bit ADCs each, and direct memory access (DMA) controllers.
DC Motor Driver IC
Toshiba also recently announced a new 50-V/5-A brushed DC motor driver IC .
The device, the TB67H482FNG (datasheet linked), is a monolithic BiCD-integrated, H-bridge driver IC designed for high-power motor control applications. Built using DMOSFET-based output transistors, this IC integrates and operates as a PWM constant current control device, which precisely regulates motor current through an adjustable reference voltage at the VREF pin. Meanwhile, the current threshold is determined by an external sense resistor and configurable torque settings via the TRQ_x input pins, providing 16 discrete torque levels from 5% to 100%. The driver supports both slow and fast decay modes, which are selectable through the DECAY pin.

The TB67H482FNG block diagram.
According to the datasheet, the TB67H482FNG operates within a VM range of 8.2 V to 44 V, with an output on-resistance of 0.2 Ω per bridge (high-side low-side) at 2 A. Its switching characteristics include a rise time of 30–200 ns and a propagation delay of 400–440 ns.
A built-in 3.3-V regulator powers internal logic, while protection features include thermal shutdown (TSD), overcurrent detection (ISD), and undervoltage lockout (UVLO).
Other features include the SLEEP_X input, which minimizes power consumption by disabling the internal oscillator and output stage when inactive. Additionally, the RESET_X pin resets fault conditions related to overcurrent protection.
Supporting Motor Control
As electrification accelerates across multiple industries, precise and efficient motor control has become a necessity. With its new set of releases, Toshiba hopes to align with these industry needs and provide engineers with integrated, high-performance solutions for next-generation, motor-driven applications.